Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, which are the female reproductive organs that produce eggs. Ovarian cancer often goes undetected in its early stages, and symptoms may not be apparent until the disease has progressed. As with any cancer, early detection and treatment significantly impact outcomes. Here are key points about ovarian cancer:
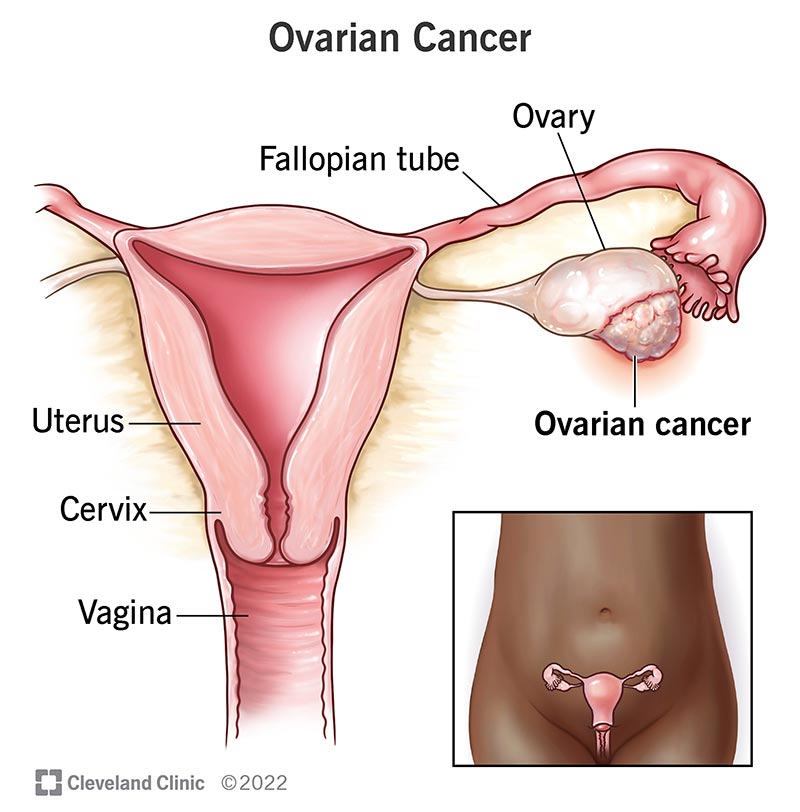
Types of Ovarian Cancer:
- The two main types are epithelial ovarian cancer (arising from the cells that cover the ovaries) and germ cell ovarian cancer (arising from the cells that produce eggs).
Risk Factors:
- Age, family history, certain genetic mutations (BRCA1 and BRCA2), personal history of breast or colorectal cancer, and certain reproductive factors can influence the risk of ovarian cancer.
Symptoms:
- Early stages may have no symptoms.
- Symptoms may include bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, and changes in urinary urgency or frequency.
Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis involves pelvic examinations, imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scan), blood tests (CA-125), and, in some cases, a biopsy.
Staging:
- Staging determines the extent of the cancer and influences treatment decisions.
- Stages range from I (early) to IV (advanced).
Treatment Options:
- Treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation therapy.
- The specific treatment plan depends on factors such as the stage of cancer and the overall health of the patient.
Genetic Testing:
- Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer may consider genetic testing for mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
Prevention:
- There is no sure way to prevent ovarian cancer, but some risk reduction strategies include using oral contraceptives, having a healthy lifestyle, and considering risk-reducing surgery for high-risk individuals.
Survival Rates:
- The prognosis for ovarian cancer depends on factors such as the stage at diagnosis and the response to treatment.
Awareness and Advocacy:
- Ovarian cancer awareness is important for early detection.
- Advocacy efforts aim to increase research funding and improve outcomes for women with ovarian cancer.





