HEAD & NECK Cancer
Head and neck cancers refer to a group of cancers that occur in the head and neck region, including the oral cavity (mouth), pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), paranasal sinuses, nasal cavity, and salivary glands. Here are key points about head and neck cancers:
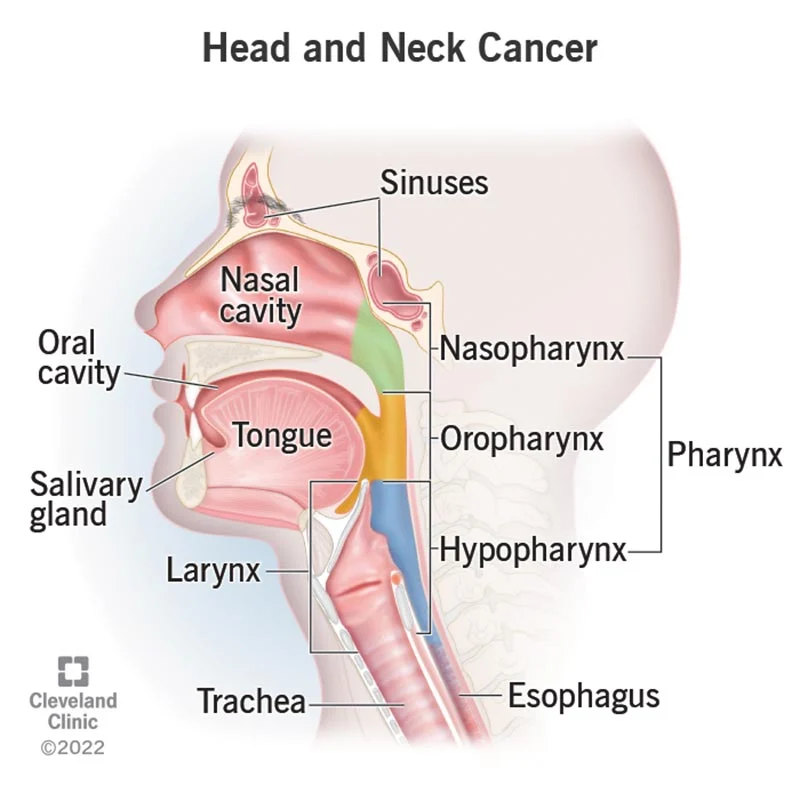
- Types of Head and Neck Cancers:
- Oral Cavity Cancer: Occurs in the lips, tongue, gums, and lining of the mouth.
- Pharyngeal Cancer: Affects the pharynx, which is the tube inside the neck that leads from the nose and mouth to the esophagus.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Originates in the larynx, which contains the vocal cords.
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer: Develops in the nasal cavity or the sinuses around the nose.
- Salivary Gland Cancer: Affects the salivary glands that produce saliva.
- Risk Factors:
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption are major risk factors, especially for cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: HPV infection, particularly with certain high-risk strains, is a risk factor for oropharyngeal cancers.
- Occupational Exposures: Exposure to certain workplace carcinogens, such as asbestos and certain chemicals, may increase the risk.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged sun exposure is a risk factor for lip cancer.
- Age: The risk of head and neck cancers increases with age.
- Gender: Men are more likely than women to develop these cancers.
- Signs and Symptoms:
- Symptoms vary depending on the location of the cancer but may include persistent pain, difficulty swallowing, changes in voice, persistent cough, unexplained weight loss, and a lump or sore that does not heal.
- Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests (CT scans, MRI, PET scans), and endoscopic procedures (laryngoscopy, pharyngoscopy).
- Biopsy samples are taken for laboratory examination to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Staging:
- Staging helps determine the extent of the cancer and guides treatment decisions.
- Treatment Options:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue is a common treatment, and it may involve removal of part or all of the affected organ.
- Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill or control cancer cells.
- Targeted Therapy: Medications that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Stimulating the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Survival Rates:
- Prognosis varies based on factors such as the type of head and neck cancer, stage at diagnosis, and response to treatment.
- Early detection is associated with better outcomes.
- Quality of Life Issues:
- Treatment for head and neck cancers may impact functions such as speech, swallowing, and breathing.
- Rehabilitation and supportive care, including speech therapy and nutritional support, are important aspects of treatment.
- Prevention:
- Avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Practicing safe sex and getting vaccinated against HPV.
- Sun protection to reduce the risk of lip cancer.





