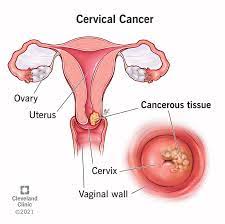
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Most cervical cancers are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. Regular screening, such as Pap smears and HPV tests, can help detect precancerous changes in the cervix early, allowing for effective intervention and prevention of cervical cancer.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- The primary cause is persistent infection with high-risk strains of HPV.
- Other risk factors include smoking, a weakened immune system, long-term use of oral contraceptives, and a family history of cervical cancer.
HPV Vaccination:
- HPV vaccines are available to protect against the most common high-risk types of the virus. Vaccination is typically recommended for adolescents.
Screening and Early Detection:
- Regular cervical cancer screening is crucial for early detection.
- Pap smears (Pap tests) and HPV tests are common screening methods.
Symptoms:
- Early stages may be asymptomatic.
- Symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, pain during intercourse, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis involves a Pap smear, HPV testing, colposcopy, and biopsy for confirmation.
Stages of Cervical Cancer:
- Staging is based on the extent of the cancer. Stages range from 0 (pre-cancer) to IV (advanced cancer).
Treatment Options:
- Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
- The choice of treatment depends on the stage and type of cervical cancer.
Prevention:
- Practice safe sex and limit the number of sexual partners.
- Quit smoking.
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
Prognosis:
- Early detection and treatment offer a better prognosis.
- Survival rates vary depending on the stage at diagnosis.
Follow-Up Care:
- After treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential to monitor for any recurrence or complications.
Global Impact:
- Cervical cancer is a significant global health issue, and efforts are ongoing to improve prevention, screening, and treatment worldwide.





